Moocable is learner-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Description
Learn how to use discrete mathematics to become a better programmer. Explore the role of math in programming, how to use discrete math to analyze data test logic, and more.
Tags
Syllabus
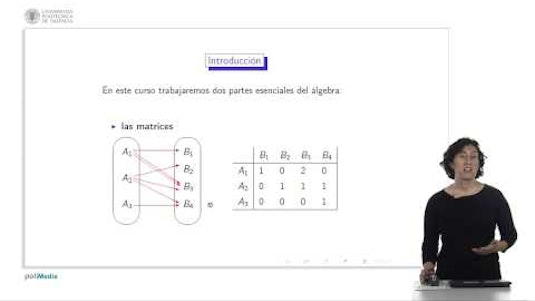
Introduction
- Welcome
- What you should know
- Using the exercise files
- Basics of discrete mathematics
- Discrete math for programming
- Real-world discrete math
- Abstract discrete math
- Objects as sets
- Set notation
- Set operations
- Power sets
- Sequences and sums
- Recursion
- Cardinality, disjointness, and partitions
- Sets from Cartesian products
- Challenge: Practice with sets
- Solution: Practice with sets
- Functional programming
- Datatypes
- Characters and strings
- Recursive functions
- Challenge: Learn SML
- Solution: Create new data types
- Use SML to create lists
- Perform functions on lists
- Create datatypes that use lists
- Challenge: Model a lunch order
- Solution: Model a lunch order
- Valid reasoning and inference
- Truth tables
- Identify and evaluate predicates
- Conditional propositions
- Valid arguments
- Rules of inference
- Prove logical equivalence
- Challenge: Write truth tables
- Solution: Write truth tables
- Write a general outline for a proof
- Write subset proofs
- Evaluate conditional proofs
- Understand biconditional proofs
- Prove with mathematical induction
- Challenge: Write a proof
- Solution: Write a proof
- Visualize data with graph theory
- Network optimization with trees
- Event probability
- Cryptography
- Challenge: Advanced techniques
- Solution: Advanced techniques
- Next steps

Programming Foundations: Discrete Mathematics
Affiliate notice
-
TypeOnline Courses
-
ProviderLinkedIn Learning
Learn how to use discrete mathematics to become a better programmer. Explore the role of math in programming, how to use discrete math to analyze data test logic, and more.
Introduction
- Welcome
- What you should know
- Using the exercise files
- Basics of discrete mathematics
- Discrete math for programming
- Real-world discrete math
- Abstract discrete math
- Objects as sets
- Set notation
- Set operations
- Power sets
- Sequences and sums
- Recursion
- Cardinality, disjointness, and partitions
- Sets from Cartesian products
- Challenge: Practice with sets
- Solution: Practice with sets
- Functional programming
- Datatypes
- Characters and strings
- Recursive functions
- Challenge: Learn SML
- Solution: Create new data types
- Use SML to create lists
- Perform functions on lists
- Create datatypes that use lists
- Challenge: Model a lunch order
- Solution: Model a lunch order
- Valid reasoning and inference
- Truth tables
- Identify and evaluate predicates
- Conditional propositions
- Valid arguments
- Rules of inference
- Prove logical equivalence
- Challenge: Write truth tables
- Solution: Write truth tables
- Write a general outline for a proof
- Write subset proofs
- Evaluate conditional proofs
- Understand biconditional proofs
- Prove with mathematical induction
- Challenge: Write a proof
- Solution: Write a proof
- Visualize data with graph theory
- Network optimization with trees
- Event probability
- Cryptography
- Challenge: Advanced techniques
- Solution: Advanced techniques
- Next steps
Tags
Related Courses


Bayesian Networks 2 - Forward-Backward - Stanford CS221: AI

Tutorials for Complex Systems

Algebra: Elementary to Advanced - Equations & Inequalities

PhETs - Interactive Simulations for Science and maths

Fundamentals of Engineering Exam Review

Causal Inference 2

Math for Machine Learning (Indonesian)

NES Essential Academic Skills Mathematics Subtest 3 (003): Practice & Study Guide

Geometry I

Linear Regression in Python

Intro to Algebra
Loading...
Saving...
Loading...
 Online Courses
Online Courses  LinkedIn Learning
LinkedIn Learning
